5G-Only Network Mode: The Future of Mobile Connectivity
The evolution of mobile communication has always followed a clear pattern: faster speeds, lower latency, and the ability to connect more devices efficiently. From 2G enabling voice calls, to 3G bringing mobile internet, and 4G transforming smartphones into powerful computing platforms, each generation has reshaped how societies communicate and operate. The introduction of 5G-Only Network Mode marks a significant shift in this evolution, representing not just an upgrade in speed, but a fundamental transformation in how mobile networks are designed and used.
Understanding 5G-Only Network Mode
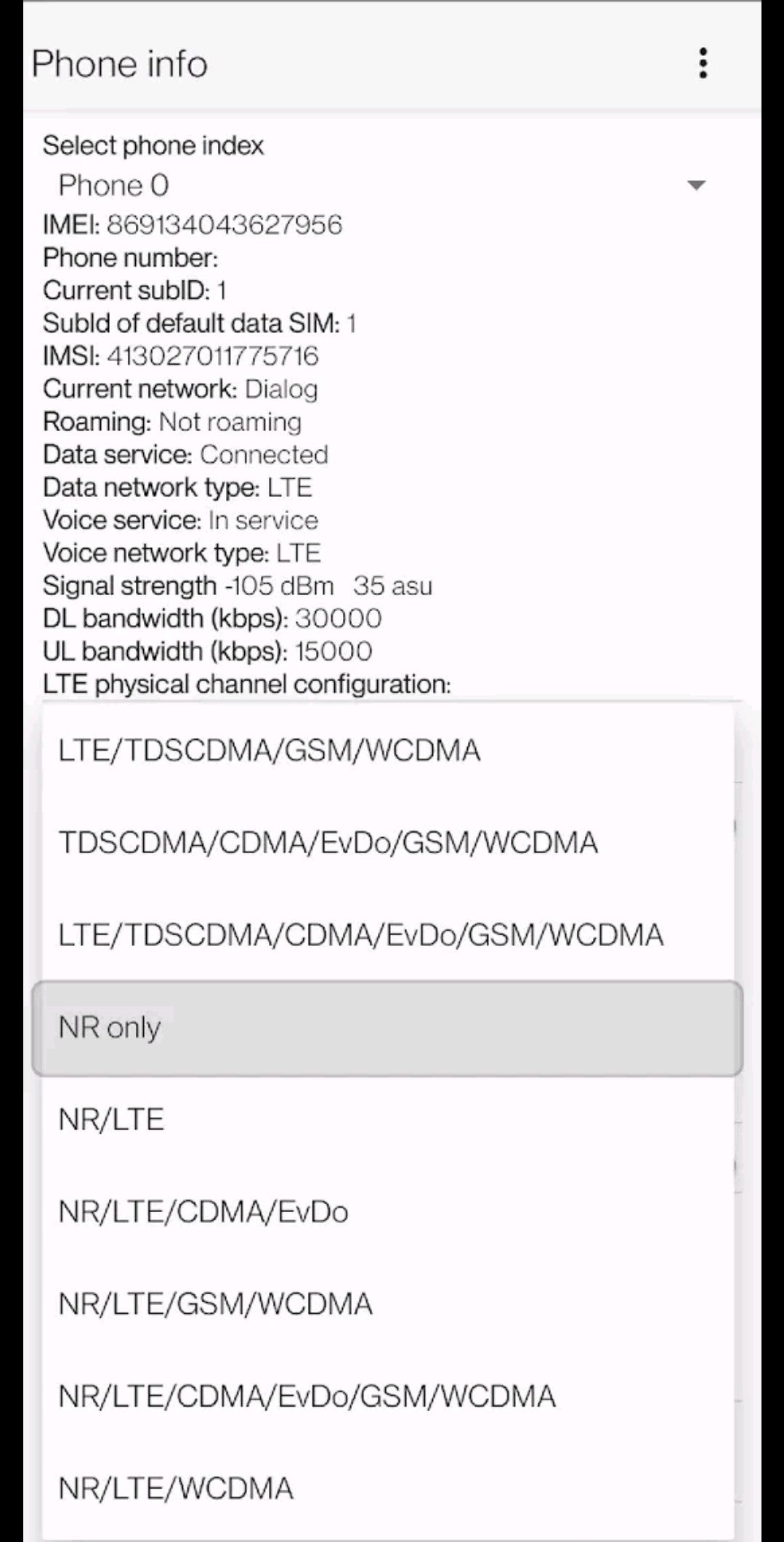
5G-Only Network Mode refers to a configuration where a mobile device connects exclusively to 5G networks and does not fall back to legacy networks such as 4G LTE, 3G, or 2G. Unlike early 5G deployments, which relied heavily on Non-Standalone (NSA) architecture using 4G core networks, 5G-Only mode typically operates on a Standalone (SA) 5G core.
In this mode, all services—including voice, data, and signaling—are handled by the 5G infrastructure. Technologies such as Voice over New Radio (VoNR) replace older systems like VoLTE, ensuring that voice communication is fully integrated into the 5G ecosystem.
Evolution from NSA to SA Networks
When 5G was first introduced, most operators adopted the NSA model to reduce deployment costs and accelerate rollout. In NSA, the 5G radio interface works alongside the existing 4G core network. While this approach delivered higher data speeds, it limited access to many of 5G’s advanced capabilities.
5G-Only Network Mode relies on Standalone (SA) architecture, which uses a native 5G core. This transition unlocks features such as ultra-low latency, massive machine-type communications (mMTC), and enhanced network slicing. As a result, 5G becomes more than just “faster 4G” and instead functions as a platform for next-generation digital services.
Key Features of 5G-Only Network Mode
1. Ultra-Low Latency
One of the defining features of 5G-Only mode is its ability to deliver latency as low as 1 millisecond in ideal conditions. This is crucial for applications that require real-time responsiveness, such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, cloud gaming, and augmented reality (AR).
2. Network Slicing
Network slicing allows operators to create multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure. Each slice can be optimized for specific use cases, such as high-speed data, low-latency communication, or massive IoT connectivity. This capability is fully realized only in a 5G-Only, Standalone environment.
3. Improved Spectral Efficiency
5G-Only networks use advanced technologies like beamforming, massive MIMO, and dynamic spectrum sharing more effectively. This leads to better utilization of available spectrum and improved performance in densely populated areas.
4. Enhanced Security
The 5G core introduces stronger encryption, improved authentication mechanisms, and better protection against signaling attacks. In 5G-Only mode, these security enhancements apply to all services, reducing reliance on older, more vulnerable protocols.
5. Native Support for IoT and Industry 4.0
5G-Only mode is particularly important for industrial automation, smart cities, and large-scale IoT deployments. It supports massive device connectivity with low power consumption, enabling sensors and machines to operate efficiently over long periods.
Benefits of 5G-Only Network Mode
For Consumers
Consumers benefit from faster and more consistent data speeds, improved call quality through VoNR, and smoother experiences in data-intensive applications such as video streaming, online gaming, and immersive AR/VR content. Reduced network congestion also improves performance during peak usage hours.
For Enterprises
Enterprises gain access to private 5G networks, tailored network slices, and reliable low-latency communication. These capabilities are essential for smart factories, logistics optimization, remote monitoring, and mission-critical communications.
For Network Operators
Operating a 5G-Only network simplifies network architecture over time by reducing the need to maintain multiple legacy systems. This leads to lower operational costs, improved energy efficiency, and greater flexibility in deploying new services.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, the adoption of 5G-Only Network Mode is not without challenges.
1. Coverage Limitations
In many regions, 5G coverage—especially Standalone 5G—is still limited. For users in rural or underserved areas, forcing a device into 5G-Only mode may result in reduced connectivity or complete signal loss.
2. Device Compatibility
Not all smartphones and IoT devices fully support 5G Standalone or VoNR. Older devices may require firmware updates or may not function properly in a 5G-Only environment.
3. Voice Service Maturity
While VoNR offers superior call quality, it is still in the early stages of deployment in many networks. In areas where VoNR is not fully supported, voice services may be unreliable in 5G-Only mode.
4. Higher Power Consumption
Early implementations of 5G chipsets may consume more power when operating exclusively on 5G networks, potentially affecting battery life. However, this issue is gradually improving with newer semiconductor designs.
Use Cases Driving 5G-Only Adoption
Smart Cities
5G-Only networks enable real-time traffic management, smart lighting, public safety monitoring, and environmental sensing. Low latency and massive connectivity are critical for managing complex urban systems efficiently.
Autonomous and Connected Vehicles
Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication relies on ultra-low latency and high reliability. 5G-Only mode provides the necessary infrastructure to support real-time decision-making and collision avoidance systems.
Healthcare and Telemedicine
Remote diagnostics, robotic surgery, and continuous patient monitoring require stable, low-latency connections. 5G-Only networks make these advanced healthcare applications more feasible and scalable.
App Link
Factories using robotics, AI-driven quality control, and real-time analytics benefit significantly from 5G-Only networks. Private 5G deployments allow industries to maintain secure, high-performance communication systems tailored to their needs.
The Future of 5G-Only Networks
As operators continue to expand Standalone 5G coverage, 5G-Only Network Mode is expected to become the default configuration for most devices. Over time, legacy networks such as 3G and even 4G will be gradually phased out, similar to how 2G networks are being retired in many countries.
The transition to 5G-Only networks also lays the groundwork for 6G, which is expected to build upon the cloud-native, software-defined architecture introduced by 5G. Technologies such as AI-driven network management, advanced sensing, and immersive digital experiences will rely heavily on the principles established by 5G-Only operation.
Conclusion
5G-Only Network Mode represents a pivotal step in the evolution of mobile communications. By moving away from legacy dependencies and embracing a fully Standalone 5G architecture, networks can unlock the true potential of 5G technology. While challenges related to coverage, device compatibility, and service maturity remain, the long-term benefits far outweigh the limitations.
As infrastructure improves and adoption increases, 5G-Only networks will serve as the backbone of future digital ecosystems, powering innovations across industries and transforming how people, machines, and systems connect in an increasingly intelligent world.